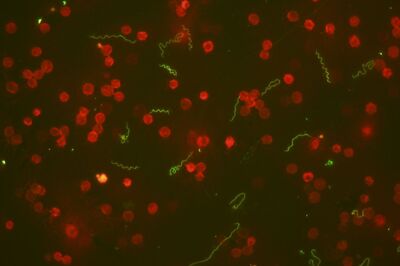
Lyme disease is a widespread multisystem disease affecting both animals and humans. In domestic animals, the disease is significant in dogs, horses, cattle and small ruminants. The causative agent of the disease is Borrelia burgdoferi, a spirochete bacterium. Borreliosis is transmitted by ticks (in the Czech republic mainly by Ixodes ricinus).
Clinical signs may appear in the animal 2-6 months after infection. In dogs, the most common symptoms are musculoskeletal problems such as lameness, swelling and joint pain, but also apathy, loss of appetite and fever. In severe cases, the kidneys, heart or brain may be affected. The severity of clinical signs depends on the immune status of the animal and the amount of pathogen ingested.